– by Pirunrat Nathchayanonth (Yori), Client Coordinator

Cord blood or Stem cell banking isn’t something new but how much do you know about it or really understand it?
Now when we talk about cord blood, we also talk about stem cells. They’re like inseparable twins. Why? Because, they are within each other!
“Cord blood contains blood (haematopoietic) stem cells, which can produce all the other cells found in blood, including cells of the immune system.” – EuroStemcell (https://www.eurostemcell.org/cord-blood-stem-cells-current-uses-and-future-challenges#:~:text=Cord%20blood%20contains%20blood%20(haematopoietic,blood%20diseases%2C%20such%20as%20leukaemia.)
For those of you who’s not that much into science like I am. Let’s get to know them better, shall we?
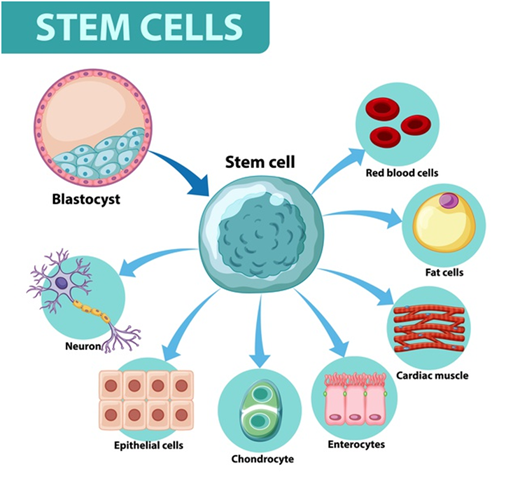
Stem cells –
They are categorized into two groups –
- Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can make several types of cells belonging to our skeletal tissues, such as cartilage, bone and fat. This includes –
- Cord Tissue – “Your baby’s umbilical cord is made of tissue and contains blood. Umbilical cord tissue is home to several cell types, including mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which scientists think may be great at acting like a body’s emergency medical team.” – CBR (https://www.cordblood.com/benefits-cord-blood/cord-tissue)
- Amniotic Membrane – Amniotic membrane, or amnion, is the innermost layer of the placenta and consists of a thick basement membrane and an avascular stromal matrix. Amniotic membrane transplantation has been used as a graft or as a dressing in different surgical subspecialties. – American Academy of Ophthalmology (https://eyewiki.aao.org/Amniotic_Membrane_Transplant)
- Adipose – Adipose tissue (AT) is considered one of the largest endocrine organs in the body as well as an active tissue for cellular reactions and metabolic homeostasis rather than an inert tissue for energy storage. The functional pleiotropism of AT relies on its ability to synthesize and release a large number of hormones, cytokines, extracellular matrix proteins and growth and vasoactive factors, collectively termed adipokines, that influence a variety of physiological and pathophysiological processes. – Science Direct (https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/adipose-tissue
- Hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) – These are the blood cell-forming adult stem cells found in bone marrow (a spongy tissue found in the centre of some bones)that can turn into different types of blood cells.
The 3 main types of blood cell they can become are:
- red blood cells – which carry oxygen around the body. – NSH (https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/stem-cell-transplant/)
- white blood cells – which collectively function as body immune system
- platelets – which work for blood clotting process
In normal adult, HSC is not circulating in blood stream but only resides in Bone Marrow.
In new born baby, just after delivery, HSC remains in umbilical vein which is the only chance to collect HSC (as umbilical cord blood) without pain.
I’m sure you’re familiar with the following –
- Cord blood – “Cord blood is the blood that remains in the placenta and umbilical cord following the birth of your baby.” – NSH (https://www.nhsbt.nhs.uk/cord-blood-bank/what-is-cord-blood/)
- Bone marrow – is part of our immune system which protects us from infection and disease. It is found inside our bones, mainly in the hip bone and the breast bone. The bone marrow is where stem cells are made. – MacMillan Cancer Support (https://www.macmillan.org.uk/cancer-information-and-support/treatment/types-of-treatment/stem-cell-and-bone-marrow-transplants/stem-cells-and-bone-marrow)
But because July is the Cord Blood awareness month, we will focus on this one in particular.
What’s the fuss?
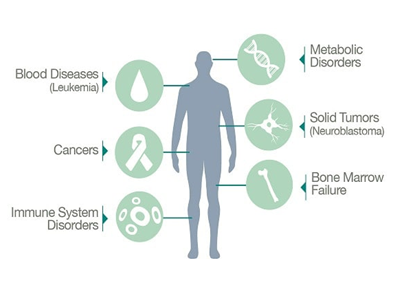
“Currently, cord blood stem cells have been approved by the FDA in the treatment of nearly 80 diseases. In addition to these approved therapies, there are close to 350 clinical trials underway investigating the use of umbilical cord blood and umbilical cord tissue for stem cell transplantation, and this number promises to steadily increase. Cord blood stem cells are approved for numerous types of malignancies, anemias, inherited metabolic disorders and deficiencies of the immune system. The majority of cord blood transplants to date have been performed in patients younger than 18 years; however, advancements in regenerative medicine show promise for all ages.” – Cryo-cell International (https://www.cryo-cell.com/treatments-and-research)
For years, countless of research has been conducted to find the cure for nasty disease like cancer and the answer lies in the one thing that we were born with!
Since most of this is placenta harvest and samples are normally being collected at birth, this should be one of the steps in your family planning. So where do we start?
Look into Cord Blood or Stem Cells Banking
“Cord blood banking, sometimes called stem cell banking or stem cell preservation, is the process of collecting the blood that remains in the umbilical cord, processing the blood to extract the stem cells, and cryogenically freezing the cells for potential future medical use.” – ViaCord (https://www.viacord.com/why-bank/cord-blood/)
https://www.cordbloodbank.com/what-are-stem-cells/what-is-cord-blood/
If you’re in Thailand and you don’t know where to start, please allow us to direct you to Cryoviva (http://cryoviva.com/), one of our longest running partners specializes in this field. With internationally renowned standards and innovative procedure, they’re the leader in the region.
At Cryoviva, “Your Life is Your Choice”! With 12 years of experience and being one of the world’s top 10 Stem Cell storage company including many recognitions from certified institute worldwide, rest assured you have nothing to worry about.

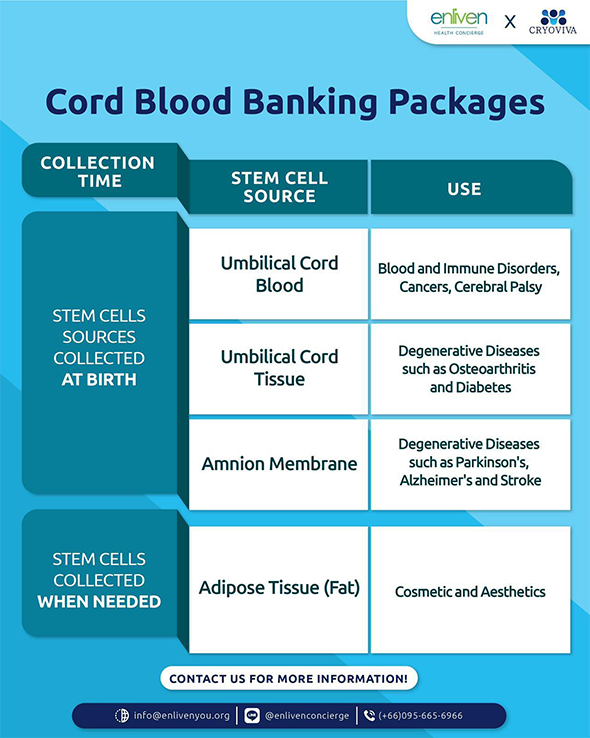
Exclusively for Enliven clients we are now offering 4 Special Cord Blood Banking Packages available for both MSCs and HSCs. Contact us now for more details!